This article outlines instructions to configure a client VPN connection on commonly-used operating systems. For more information about client VPN, please refer to our Client VPN Overviewdocumentation.
For troubleshooting, please refer to our Troubleshooting Client VPN documentation.
Android
To configure an Android device to connect to the Client VPN, follow these steps:
- Navigate to Settings -> Wireless & Networks -> VPN
- Click the Plus Icon to add an additional VPN profile
Simple to deploy and operate, the Cisco VPN Client enables customers to establish secure, end-to-end encrypted tunnels to Cisco remote access VPN devices supporting the Unified Client Framework. Setting up the Cisco VPN client. Download the Cicso VPN client for macOS from our Self Registration page. Launch the downloaded installer file and click through the screens to complete the installation. Go to your Applications folder and open the Cisco folder. Double-click on the Cisco AnyConnect Secure Mobility Client. Enter vpn.ox.ac.uk into.
- YOU CAN REVIEW PRODUCT DESCRIPTION OF Cisco Asa Vpn Client For Mac And Cisco Asdm Site To Site Vpn Reset Button HERE.
- Installing the Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client. Note: Use the Safari browser when downloading this software. ONLY Mac OS 10.9.x and newer versions are supported by the CISCO AnyConnect software. Download the Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client installer for Mac. Enter the CougarNet credentials. Click the AnyConnect VPN link to download the software. If you get a DMG file double click the.
Name: This can be anything you want to name this connection, for example, 'Work VPN.'
Type: select L2TP/IPSEC PSK
Server address: Enter the hostname (e.g. .com)orthe active WAN IP (e.g. XXX.XXX.XXX). Hostname is encouraged instead of active WAN IP because it is more reliable in cases of WAN failover. Admin can find them in Dashboard, under Security appliance > Monitor > Appliance status.
IPSec pre-shared key: Enter the pre-shared key that admin created in Security appliance >Configure > Client VPN settings.
Press save
You will be prompted for user credentials when you connect.
Chrome OS
Chrome OS based devices can be configured to connect to the Client VPN feature on MX Security Appliances. This allows remote users to securely connect to the LAN. This article will cover how to configure the VPN connection on a Chrome OS device. For more information on how to setup the Client VPN feature of the MX or how to connect from other operating systems, please visit the MX documentation.
- If you haven't already, sign in to your Chromebook.
- Click the status area at the bottom of your screen, where your account picture is located.
- Select Settings.
- In the 'Internet connection' section, click Add connection.
- Select Add private network.
- In the box that appears, fill in the information below:
- Server hostname:Enter the hostname (e.g. .com)orthe active WAN IP (e.g. XXX.XXX.XXX). Hostname is encouraged instead of active WAN IP because it is more reliable in cases of WAN failover. Admin can find them in Dashboard, under Security appliance > Monitor > Appliance status.
- Service name: This can be anything you want to name this connection, for example, 'Work VPN.'
- Provider type: Select L2TP/IPsec + Pre-shared key.
- Pre-shared key: Enter shared secret that admin created in Security appliance >Configure > Client VPN settings.
- Username credentials for connecting to VPN. If using Meraki authentication, this will be an e-mail address.
- Password credentials for connecting to VPN.
- Click Connect.
For more information regarding the configuration of VPN connections in Chrome OS, visit the Google Support page.
To configure an iOS device to connect to the Client VPN, follow these steps:
- Navigate to Settings -> General-> VPN -> Add VPN Configuration...
- Type: set to L2TP.
- Description:This can be anything you want to name this connection, for example, 'Work VPN.'
- Server: Enter the hostname (e.g. .com)orthe active WAN IP (e.g. XXX.XXX.XXX). Hostname is encouraged instead of active WAN IP because it is more reliable in cases of WAN failover. Admin can find them in Dashboard, under Security appliance > Monitor > Appliance status.
- Account: Enter the username
- Password: Enter if desired. If the password is left blank, it will need to be entered each time the device attempts to connect to the Client VPN.
- Secret: Enter shared secret that admin created in Security appliance >Configure > Client VPN settings.
- Ensure that Send All Traffic is set to On.
- Save the configuration.
macOS
Currently only the following authentication mechanisms are supported:

- User authentication: Active Directory (AD), RADIUS, or Meraki hosted authentication.
- Machine authentication: Preshared keys (a.k.a., shared secret).
When using Meraki hosted authentication, VPN account/user name setting on client devices (e.g., PC or Mac) is the user email address entered in the Dashboard.
The instructions below are tested on Mac OS 10.7.3 (Lion).
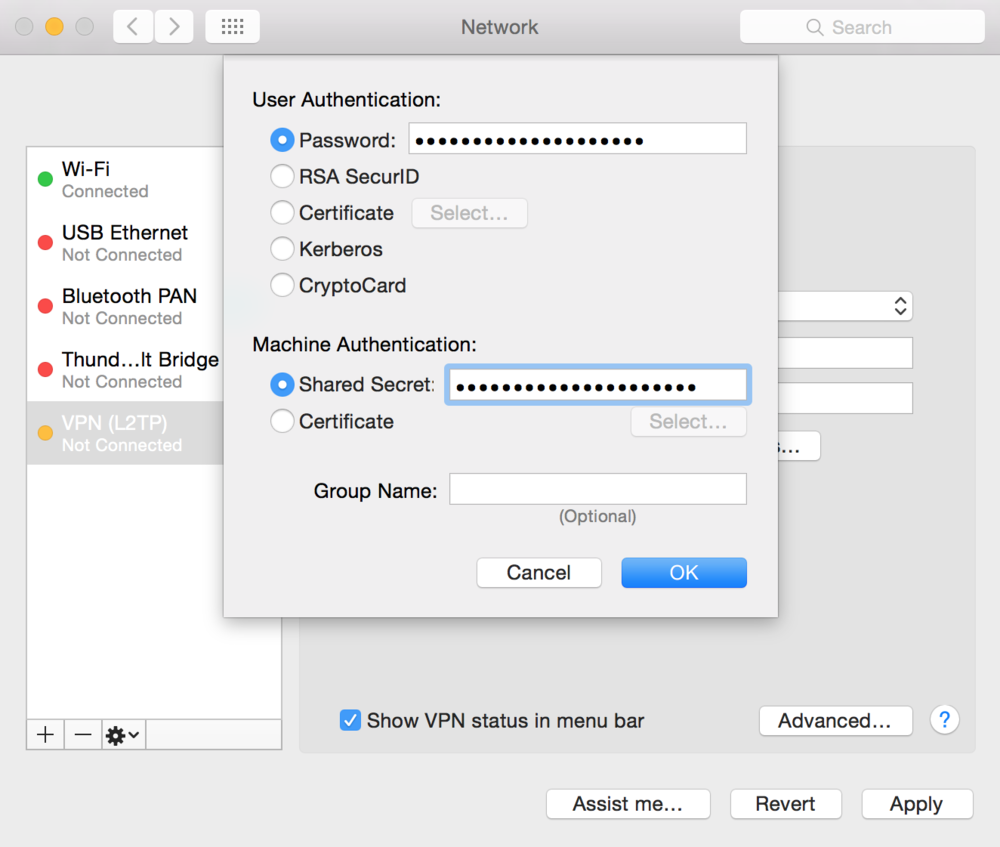
Open System Preferences > Network from Mac applications menu. Click the '+' button to create a new service, then select VPN as the interface type, and choose L2TP over IPsec from the pull-down menu.
- Server Address: Enter the hostname (e.g. .com)orthe active WAN IP (e.g. XXX.XXX.XXX). Hostname is encouraged instead of active WAN IP because it is more reliable in cases of WAN failover. Admin can find them in Dashboard, under Security appliance > Monitor > Appliance status.
- Account Name: Enter the account name of the user (based on AD, RADIUS or Meraki Cloud authentication).
- User Authentication > Password: User password (based on AD, RADIUS or Meraki Cloud authentication).
- Machine Authentication > Shared Secret: Enter shared secret that admin created in Security appliance >Configure > Client VPN settings.
The VPN connectivity will not be established if you don't enable the Send all traffic over VPN connection option!
Windows 7
Currently only the following authentication mechanisms are supported:
- User authentication: Active Directory (AD), RADIUS, or Meraki hosted authentication.
- Machine authentication: Preshared keys (a.k.a., shared secret).
When using Meraki hosted authentication, VPN account/user name setting on client devices (e.g., PC or Mac) is the user email address entered in the Dashboard.
Open Start Menu > Control Panel, click on Network and Internet, click on View network status and tasks.
In the Set up a connection or network pop-up window, choose Connect to a workplace (Set up a dial-up or VPN connection to your workplace).
Choose Use my Internet connection (VPN), in the Connect to a workspace dialog window.
In the Connect to a Workplace dialog box, enter:
- Internet address: Enter the hostname (e.g. .com)orthe active WAN IP (e.g. XXX.XXX.XXX). Hostname is encouraged instead of active WAN IP because it is more reliable in cases of WAN failover. Admin can find them in Dashboard, under Security appliance > Monitor > Appliance status.
- Destination name:This can be anything you want to name this connection, for example, 'Work VPN.'
Choose 'Don't connect now; just set it up so that I can connect later' option.
Click Next. In the next dialog window, enter the user credentials, and click Create.
Despite the name 'Unencrypted PAP', the client's password is sent encrypted over an IPsec tunnel between the client device and the MX. The password is fully secure and never sent in clear text over either the WAN or the LAN.
Windows 8
Currently only the following authentication mechanisms are supported:
- User authentication: Active Directory (AD), RADIUS, or Meraki hosted authentication.
- Machine authentication: Preshared keys (a.k.a., shared secret).
When using Meraki hosted authentication, VPN account/user name setting on client devices (e.g., PC or Mac) is the user email address entered in the Dashboard.
Open Start Menu > Network and Sharing Center and click Settings.
In the Set Up a Connection or Network pop-up window, choose Connect to a workplace.
(Set up a dial-up or VPN connection to your workplace).
Choose Use my Internet connection (VPN), in the Connect to a Workspace dialog window.
In the Connect to a Workplace dialog box, enter:
- Internet address: Enter the hostname (e.g. .com)orthe active WAN IP (e.g. XXX.XXX.XXX). Hostname is encouraged instead of active WAN IP because it is more reliable in cases of WAN failover. Admin can find them in Dashboard, under Security appliance > Monitor > Appliance status.
- Destination name:This can be anything you want to name this connection, for example, 'Work VPN.'
Go back to Network and Sharing Center and click Change Adapter Settings.
Despite the name 'Unencrypted PAP', the client's password is sent encrypted over an IPsec tunnel between the client device and the MX. The password is fully secure and never sent in clear text over either the WAN or the LAN.
Windows 10
Currently only the following authentication mechanisms are supported:
- User authentication: Active Directory (AD), RADIUS, or Meraki hosted authentication.
- Machine authentication: Preshared keys (a.k.a., shared secret).
When using Meraki hosted authentication, VPN account/user name setting on client devices (e.g., PC or Mac) is the user email address entered in the Dashboard.
Open Start Menu > Search 'VPN' > Click Change virtual private networks (VPN)
From the VPN settings page, click Add a VPN connection.
In the Add a VPN connection dialog:
- VPN provider: Set to Windows (built-in)
- Connection name: This can be anything you want to name this connection, for example, 'Work VPN.'
- Server name or address: Enter the hostname (e.g. .com)orthe active WAN IP (e.g. XXX.XXX.XXX). Hostname is encouraged instead of active WAN IP because it is more reliable in cases of WAN failover. Admin can find them in Dashboard, under Security appliance > Monitor > Appliance status.
- VPN type: Select L2TP/IPsec with pre-shared key
- User name and Password: optional
Press Save.
After the VPN connection has been created, click Change adapter options under Related settings.
Right-click on the VPN Connection from the list of adapters and click Properties.
Despite the name 'Unencrypted PAP', the client's password is sent encrypted over an IPsec tunnel between the client device and the MX. The password is fully secure and never sent in clear text over either the WAN or the LAN.
In Advanced Properties dialog box, choose 'Use preshared key for authentication' and enter the pre-shared key that admin created in Security appliance >Configure > Client VPN settings.
Back at the Network Connections window, right-click on the VPN connection and click Connect / Disconnect.
Find your VPN profile and click Connect.
Vpn Cisco Client For Mac High Sierra
Windows XP
Currently only the following authentication mechanisms are supported:
- User authentication: Active Directory (AD), RADIUS, or Meraki hosted authentication.
- Machine authentication: Preshared keys (a.k.a., shared secret).
When using Meraki hosted authentication, use the email address for VPN account / user name.
Open Start Menu > Control Panel, click on Network Connections.
In the Network Tasks section, click on Create a new connection.
Choose Connect to the network at my workplace, in the New Connection Wizard window.
Choose Virtual Private Network connection in the next section.
Then, give a name for this connection. This can be anything you want to name this connection, for example, 'Work VPN.'
Enter the hostname (e.g. .com)orthe active WAN IP (e.g. XXX.XXX.XXX). Hostname is encouraged instead of active WAN IP because it is more reliable in cases of WAN failover. Admin can find them in Dashboard, under Security appliance > Monitor > Appliance status.
In the Connect <Connection Name> box, click on Properties
In the General tab, verify the hostname (e.g. .com)orthe active WAN IP (e.g. XXX.XXX.XXX). Hostname is encouraged instead of active WAN IP because it is more reliable in cases of WAN failover. Admin can find them in Dashboard, under Security appliance > Monitor > Appliance status.
Despite the name 'Unencrypted PAP', the client's password is sent encrypted over an IPsec tunnel between the client device and the MX. The password is fully secure and never sent in clear text over either the WAN or the LAN.
Cisco Vpn Client For Mac Os Mojave
Linux
Since Client VPN uses the L2TP over IPsec standard, any Linux client that properly supports this standard should suffice. Please note that newer versions of Ubuntu do not ship with a VPN client that supports L2TP/IP, and will therefore require a 3rd party VPN client that supports the protocol.
Note: The xl2tp package does not send user credentials properly to the MX when using Meraki Cloud Controller authentication, and this causes the authentication request to fail. Active Directory or RADIUS authentication can be used instead for successful authentication.
Cisco AnyConnect is the recommended VPN client for Mac. The built-in VPN client for Mac is another option but is more likely to suffer from disconnects.
Overview
Stanford's VPN allows you to connect to Stanford's network as if you were on campus, making access to restricted services possible. To connect to the VPN from your Mac you need to install the Cisco AnyConnect VPN client.
Two types of VPN are available:
- Default Stanford (split-tunnel). When using Stanford's VPN from home, we generally recommend using the Default Stanford split-tunnel VPN. This routes and encrypts all traffic going to Stanford sites and systems through the Stanford network as if you were on campus. All non-Stanford traffic proceeds to its destination directly.
- Full Traffic (non-split-tunnel). This encrypts all internet traffic from your computer but may inadvertently block you from using resources on your local network, such as a networked printer at home. If you are traveling or using wi-fi in an untrusted location like a coffee shop or hotel, you may wish to encrypt all of your internet traffic through the Full Traffic non-split-tunnel VPN to provide an additional layer of security.
You can select the type of VPN you want to use each time you connect.
Install the VPN client
- Download the Cisco AnyConnect installer for Mac.
- Double-click the InstallAnyConnect.pkg file to start the Cisco AnyConnect Installer wizard.
- When the Welcome window displays, click Continue.
- Select your hard drive as the destination where you want to install Cisco AnyConnect and then click Continue.
- Click Install to perform a standard installation of the software.
- At the prompt, enter your administrator account password for the Mac and click Install Software.
- When the software has finished installing, click Close.
Connect to the Stanford VPN
- To launch the VPN client, open your Applications folder and navigate to Cisco > Cisco AnyConnect Secure Mobility Client.app.
- When prompted for a VPN, enter su-vpn.stanford.edu and then click Connect.
- Enter the following information and then click OK:
- Group: select Default Stanford split- tunnel (non-Stanford traffic flows normally on an unencrypted internet connection) or Full Traffic non-split-tunnel (all internet traffic flows through the VPN connection)
- Username: your SUNet ID
- Password: your SUNet ID password
- Next, the prompt for two-step authentication displays.
- Enter a passcode or enter the number that corresponds to another option(in this example, enter 1 to authenticate using Duo Push on an iPad). You may have to scroll down the list to see all of your options. Then click Continue.
- If your only registered authentication method is printed list, hardware token, or Google Authenticator, the menu does not display. Enter a passcode in the Answer field and click Continue.
- Click Accept to connect to the Stanford Public VPN service.
- Once the VPN connection is established, the Cisco AnyConnect icon with a small lock appears in the dock.
Cisco Vpn Software For Mac
Disconnect from the Stanford VPN
- Click the Cisco AnyConnect icon with a small lock.
- At the prompt, click Disconnect.
